The right choice between polypropylene (PP) compounds and ABS compounds depends on performance requirements for your end-use, especially in automotive parts, electrical enclosures, and appliance housings. By comparing key properties like impact strength, heat resistance, and processability, you can select the best-fit PP injection molding compound or impact-modified ABS grade with confidence.
Understanding Polypropylene (PP) Compounds
Polypropylene has earned its reputation in the plastic industry for its lightweight, versatility and toughness. PP compounds dominate applications where flexibility meets durability.
Key Properties of Polypropylene
Polypropylene’s molecular structure gives polypropylene compounds a versatile performance profile for real-world manufacturing. With excellent chemical resistance, PP compounds withstand acids, alkalis, and many organic solvents that can degrade lower-grade plastics. PP also has a low density (around 0.9 g/cm³), making it one of the lightest thermoplastics available, which is a major advantage when weight reduction matters in automotive components and even aerospace applications.
Another key strength of polypropylene (PP) compounds is fatigue resistance. A well-formulated PP engineering compound can flex repeatedly without cracking, which makes it ideal for living hinges used in flip-top bottles and containers. Add strong moisture resistance and you get a PP injection molding compound that performs consistently across varied environments. In terms of temperature performance, polypropylene typically operates between -20°C to 100°C, while heat-stabilized PP grades and other specialized formulations can extend these limits further.
Industrial Applications of PP
Polypropylene compounds are found across most manufacturing facilities because PP compounds are easy to process, cost-effective, and reliable in high-volume production. The automotive sector uses polypropylene (PP) compounds extensively for battery cases, bumpers and trims, interior parts, and under-the-hood components where chemical resistance and durability matter. In packaging, PP injection molding compound grades and food-safe variants make polypropylene a go-to choice for containers, caps, closures, and films.
In the medical sector, manufacturers value PP engineering compound options for sterilizability and biocompatibility in syringes, vials, and diagnostic components. The textile industry relies on polypropylene fibres for carpets and non-woven fabrics used in hygiene and industrial applications. Even reusable shopping bags commonly contain polypropylene compounds, often tailored with additives for strength and consistent performance.
Understanding ABS Compounds
If polypropylene is the versatile workhorse, ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is the sophisticated performer, offering superior aesthetics and processing characteristics that make it a designer’s dream material.
Core Properties of ABS
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a terpolymer, meaning it combines three monomers to create a material that is greater than the sum of its parts. The Acrylonitrile provides chemical and thermal resistance, Butadiene adds impact strength and toughness, while styrene contributes rigidity and processability. Well, the result? A material with excellent dimensional stability, high impact strength (especially at low temperatures) and a surface finish straight out of the Mold. ABS accepts paint, adhesives and metallisation beautifully, for instance try chrome-plating polypropylene and you will quickly appreciate this difference. With a density around 1.05 g/cm³, it’s slightly heavier than PP but still reasonably lightweight.
ABS operates well between -20°C to 80°C, though heat deflection temperatures vary by grade. Its rigidity and strength make it ideal for structural applications where PP might flex too much.
Common Uses of ABS in Manufacturing
The keyboard on your laptop could be made from ABS compounds. Consumer electronics manufacturers prefer ABS engineering compound grades for excellent surface finish and their ability to hide injection points, which helps deliver clean, premium-looking parts. From computer housings to phone cases and other outer shells, ABS injection molding compound options support tight tolerances, consistent color, and a high-quality aesthetic.
The automotive industry uses ABS compounds for dashboards, instrument panels, and decorative trims where appearance and dimensional stability matter. Appliance manufacturers rely on ABS compounds for refrigerator liners, vacuum cleaners, and small appliance bodies that need a durable, smooth finish. In toys, LEGO bricks are one of the most famous ABS compound applications, demonstrating long-term durability and precision molding performance.
Polypropylene vs ABS: Detailed Comparison
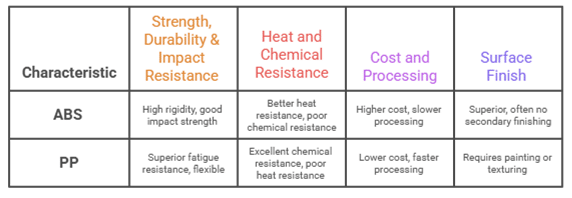
Strength, Durability & Impact Resistance
ABS compounds typically win on rigidity and impact strength, especially in cold environments. Drop an ABS part at -20°C and it is more likely to hold up, whereas some polypropylene compounds can turn brittle at low temperatures depending on grade and formulation. On the other hand, PP compounds offer natural flexibility and superior fatigue resistance, so a well-chosen PP engineering compound can bend repeatedly without cracking under cyclic loads.
Here’s a simple way to compare them without oversimplifying the performance. ABS compounds behave like a rigid, sturdy material that holds shape under load, while polypropylene (PP) compounds behave like a flexible material that absorbs repeated stress through controlled deflection. If your application needs rigidity, surface stability, and structural integrity, ABS engineering compound grades are often the better fit. If your part needs flex, snap action, or living hinges, PP injection molding compound grades usually dominate.
Heat and Chemical Resistance
PP takes the crown for chemical resistance. It stands up to most chemicals that would attack ABS, making it essential for automotive fuel systems and chemical handling equipment. ABS, however, offers better heat resistance in the 80-100°C range and superior dimensional stability under thermal cycling.
UV resistance? Both need help. Untreated PP and ABS will degrade under prolonged sun exposure, though UV-stabilized grades of each are readily available for outdoor applications.
Cost and Processing Differences
Generally, PP compounds cost less per kilogram than ABS. PP also processes faster with shorter cycle times, translating to higher productivity and lower manufacturing costs. The superior surface finish of ABS often eliminates secondary finishing operations. The glossy, professional appearance straight from the mold can offset the higher material cost. PP normally requires painting or texturing for premium aesthetics.
PP vs ABS for Popular Applications
Automotive Parts
PP’s chemical resistance can handle oil, coolant fuel exposure that probably ABS cannot match. Bumper covers? PP, for its impact resistance and repairability. The interior parts like the dashboards and trim, ABS wins with superior aesthetics and rigidity.
Electronics & Appliances
PP is used in internal components, cable management and applications requiring flexibility or chemical exposure. ABS , given its dimensional stability ensures tight tolerances for snap fits and screws.
Indoor vs Outdoor Performance
Indoors, both materials perform excellently with proper grade selection. Outdoors, UV-stabilized PP generally outlasts ABS in direct sunlight exposure. For marine applications or constant moisture exposure, PP’s superior moisture resistance gives it the edge.
How to Choose the Right Compound for Your Application
Material Selection Checklist
Start by asking the critical questions to shortlist the right option between polypropylene compounds and ABS compounds. What temperature range will the part experience, including cold impact conditions and peak operating heat? What chemicals, oils, cleaners, or solvents will it contact? Are there impact requirements, compliance needs, or safety standards that the material must meet? Finally, define the expected lifespan and whether the part must retain dimensional stability over time as a finished PP compound or ABS engineering compound component.
Next, evaluate aesthetics and fit-for-purpose. Does the product need a premium surface finish and consistent color, or is function over form acceptable? ABS compounds are often chosen where surface quality matters, while PP compounds can be ideal for functional parts where light weight and chemical resistance lead. Also think about assembly methods. Will the part use adhesives, welding, or mechanical fasteners? Both ABS injection molding compound and PP injection molding compound grades have different bonding and joining preferences, so process compatibility matters.
Performance Requirements and Cost Balance
The cheapest polymer on paper is not always the most economical in production. Balance performance requirements with total cost by factoring in processing efficiency, cycle time, scrap rates, and secondary operations. For example, using ABS compounds that reduce surface defects can lower finishing or repainting needs, while selecting the right polypropylene compounds can cut weight and material usage in high-volume parts. In many cases, a slightly higher material cost that prevents field failures or reduces warranty claims delivers a better total cost of ownership.
Whenever possible, prototype with the actual grade you plan to mold. Real-world testing often reveals details that datasheets miss, especially for impact, fit, and long-term performance. If you have specialized needs, consult compounding experts who can customize polypropylene or ABS compounds with additives like impact modifiers, heat stabilizers, UV stabilizers, or flame-retardant packages to match your application precisely.
Need Custom PP or ABS Compounds?
Get Tailored Compounding Solutions
A truly optimised performance often requires custom compounding. Whether it’s specific colour matching, flame retardancy or the enhanced UV protection and the mechanical properties, it’s always the custom formulations that can give a competitive edge.
At cmmai, we specialise in creating tailored PP and ABS compounds that meet your exact specifications. Our technical team works closely with you to understand your application specifications, requirements and then we develop compounds that deliver optimal performance at competitive costs.
Ready to optimize your material selection? Contact our experts today for a consultation on custom polypropylene or ABS compounds designed specifically for your application. Because sometimes, the best choice isn’t PP or ABS, it’s the right compound engineered just for you.